Pemvidutide: How It Differs From Other Weight Loss and Diabetes Medications
The rise of GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic® (semaglutide) and Mounjaro® (tirzepatide) has transformed the way we treat obesity and type 2 diabetes. But now, another player is entering the scene: pemvidutide. Currently in late-stage clinical trials, pemvidutide has generated excitement for its unique mechanism and impressive early results in both weight reduction and liver health.
So, how does pemvidutide differ from other medications like semaglutide, tirzepatide, and emerging drugs such as retatrutide or orforglipron? Let’s dive into the science, results, and future potential of this promising treatment.
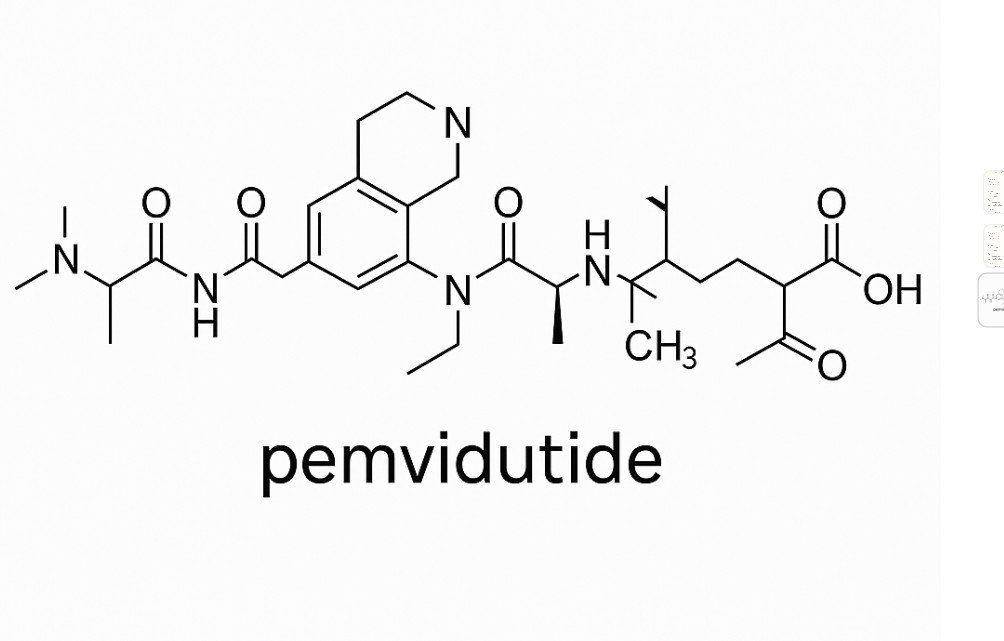
What is Pemvidutide?
Pemvidutide (developed by Altimmune) is an injectable peptide-based therapy that belongs to the incretin mimetic family, but with a twist. Like semaglutide and tirzepatide, it acts on GLP-1 receptors, but it also targets a second receptor pathway: the glucagon receptor.
This makes it a dual agonist therapy, combining the appetite-suppressing and insulin-regulating effects of GLP-1 with the metabolism-boosting effects of glucagon.
How Pemvidutide Works
- GLP-1 Activation
- Suppresses appetite
- Slows gastric emptying
- Improves blood sugar control
- Increases satiety
- Glucagon Activation
- Boosts energy expenditure
- Enhances fat burning
- Promotes liver fat reduction
Together, these actions result in both caloric intake reduction and increased energy expenditure, a powerful combination for weight loss.
Pemvidutide vs. Other Medications
1. Pemvidutide vs. Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy)
- Semaglutide: Works only on GLP-1 receptors. Highly effective for appetite suppression and blood sugar control but does not significantly increase energy expenditure.
- Pemvidutide: Works on both GLP-1 and glucagon receptors, giving it an edge in metabolism boosting and liver fat reduction.
👉 Translation: While semaglutide is excellent for weight loss, pemvidutide may offer more benefits for fat metabolism and NAFLD/NASH patients.
2. Pemvidutide vs. Tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound)
- Tirzepatide: A dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonist. The GIP pathway enhances insulin sensitivity and fat metabolism.
- Pemvidutide: Instead of GIP, it pairs GLP-1 with glucagon activation, focusing on energy expenditure and fat burning.
👉 Key difference: Tirzepatide is about insulin and fat storage control, while pemvidutide emphasizes fat burning and liver health.
3. Pemvidutide vs. Retatrutide
- Retatrutide: A triple agonist (GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon).
- Pemvidutide: A dual agonist (GLP-1 and glucagon).
👉 Retatrutide may eventually prove more powerful for overall weight loss due to its triple targeting, but pemvidutide offers a more focused approach with potentially fewer GI side effects.
4. Pemvidutide vs. Orforglipron
- Orforglipron: An oral, non-peptide GLP-1 receptor agonist still in trials. Taken daily as a pill.
- Pemvidutide: An injectable peptide therapy with longer half-life, requiring less frequent dosing.
👉 Main difference: Delivery method (pill vs injection) and mechanism (GLP-1 only vs GLP-1 + glucagon).
Unique Benefits of Pemvidutide
- Weight Loss
- In clinical studies, pemvidutide produced average weight loss up to 15% of body weight—comparable to leading drugs like semaglutide.
- Liver Fat Reduction
- Pemvidutide is especially promising for patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
- Trials show up to a 70% reduction in liver fat content, something other GLP-1 drugs don’t specifically target.
- Cardiometabolic Improvements
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Reduction in cholesterol and triglycerides
- Support for overall metabolic health
Side Effects
Like other incretin therapies, the main side effects of pemvidutide are GI-related:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
However, early data suggests side effect intensity may be lower compared to semaglutide or tirzepatide, especially regarding nausea. More long-term studies will confirm this.
Who Might Benefit Most from Pemvidutide?
- Patients with obesity who need significant weight reduction.
- People with type 2 diabetes seeking blood sugar and weight control.
- Patients with fatty liver disease (NAFLD/NASH) where liver fat reduction is a priority.
- Those struggling with metabolic syndrome (high cholesterol, high blood pressure, insulin resistance).
Pemvidutide in Clinical Trials
- Currently in Phase 2 and Phase 3 studies.
- Early results show comparable or superior liver health improvements compared to existing drugs.
- If approved, pemvidutide could carve a niche as the go-to therapy for patients with obesity and liver disease overlap.
The Future Outlook
With semaglutide and tirzepatide dominating headlines, it’s exciting to see pemvidutide offering a different angle. By combining GLP-1 and glucagon activity, it addresses both calorie intake and energy expenditure—potentially making weight loss more sustainable.
If FDA-approved, pemvidutide could be prescribed not just for obesity and diabetes, but also as a breakthrough in the fight against NAFLD and NASH, conditions that currently lack effective treatments.
Final Thoughts
While semaglutide suppresses appetite and tirzepatide improves insulin sensitivity, pemvidutide boosts fat burning and liver health. Each medication has strengths, and the right choice may depend on the patient’s unique needs.
The next few years will tell whether pemvidutide becomes a major competitor—or even a preferred treatment—for those battling obesity, diabetes, and liver disease.